Leukoplakia vs. Oral Candidiasis
Oral Leukoplakia
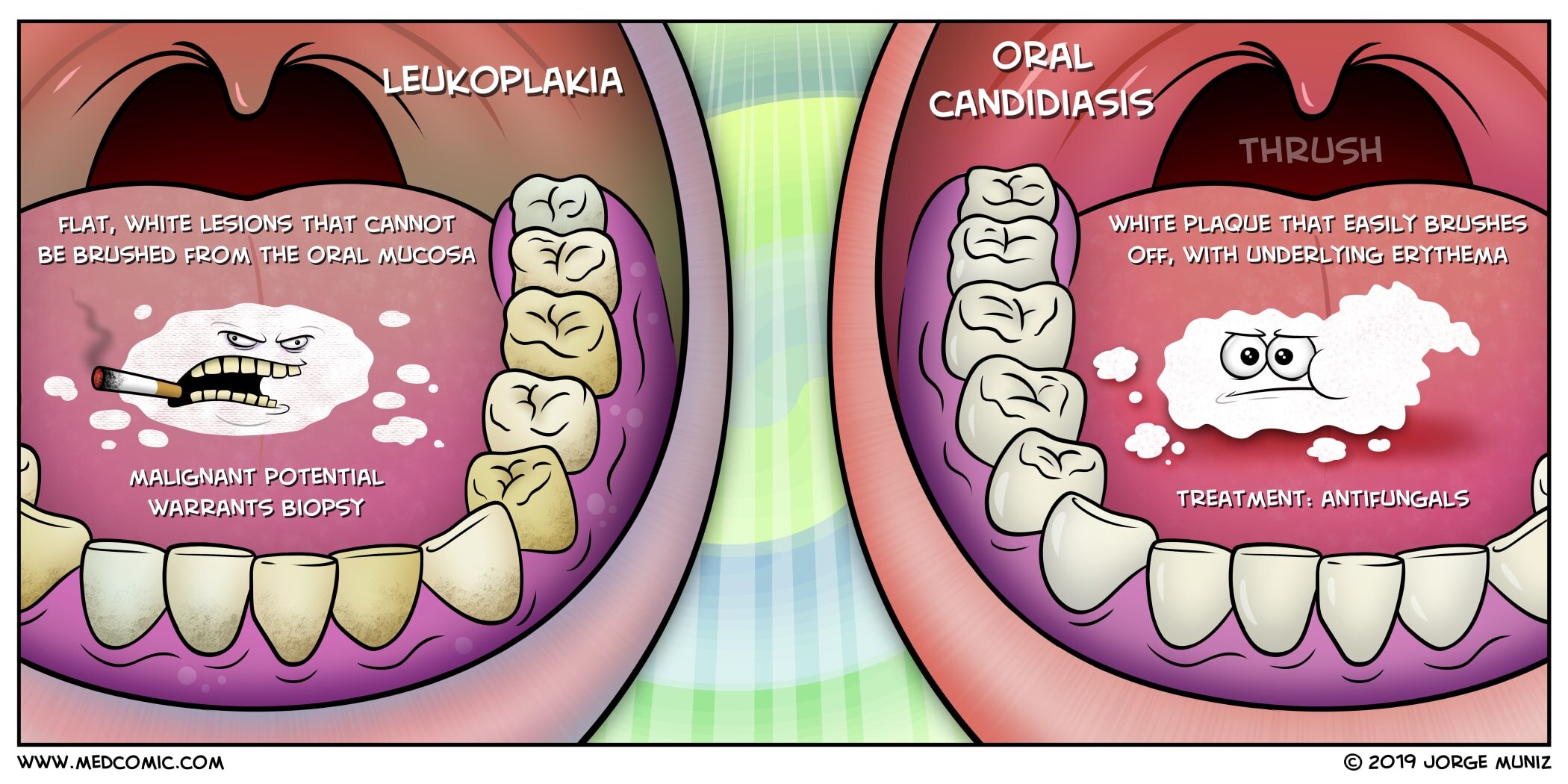
Flat, white lesions that cannot be brushed from the oral mucosa
Typically painless
Associated with tobacco and alcohol use
Associated with squamous cell carcinoma
Erythroplakia: similar lesions, but with a red appearance
Carry a higher risk of dysplasia or carcinoma
Malignant potential warrants biopsy
Management: alcohol and smoking cessation, consider surgical removal
Oral Candidiasis (Thrush)
Caused by Candida albicans
White, creamy plaque that easily brushes off, with underlying erythema
Typically associated with throat or mouth pain
Risk factors for infection
Immunocompromised states
HIV
Radiation or chemotherapy
Diabetes
Systemic or inhaled corticosteroid use
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
Dentures
Typically associated with throat or mouth pain
KOH preparation demonstrates budding yeasts, hyphae, or pseudohyphae
Treatment is with antifungals
Nystatin liquid
Oral fluconazole
Clotrimazole troches
Oral Hairy Leukoplakia
Caused by Epstein-Barr virus (human herpesvirus 4)
Most commonly affects immunocompromised patients (e.g. HIV)
White, hyperkeratotic plaque that cannot be brushed off
Usually distributed along the lateral border of the tongue
Vertical white striations may appear “hairy”
Lesions are typically painless and benign
Treatment for lesions not usually required; antivirals may be considered